Understanding and Using English Grammar - 5th Edition
1. PRESENT AND PAST; SIMPLE AND PROGRESSIVE

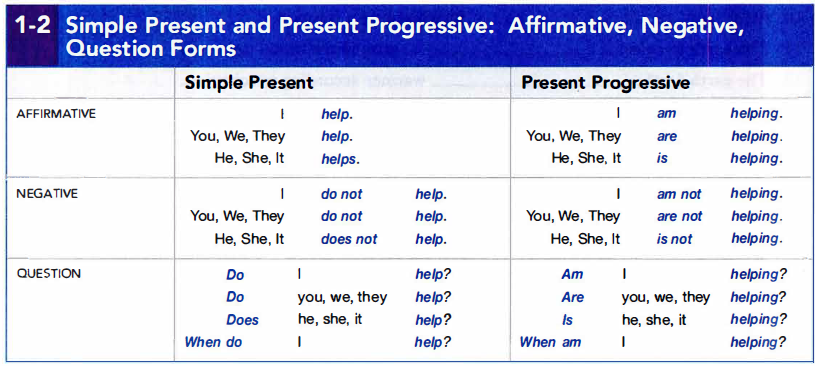
1a. Simple Present and Present Progressive

1c. Verbs not Usually used in the Progressive (Stative Verbs)


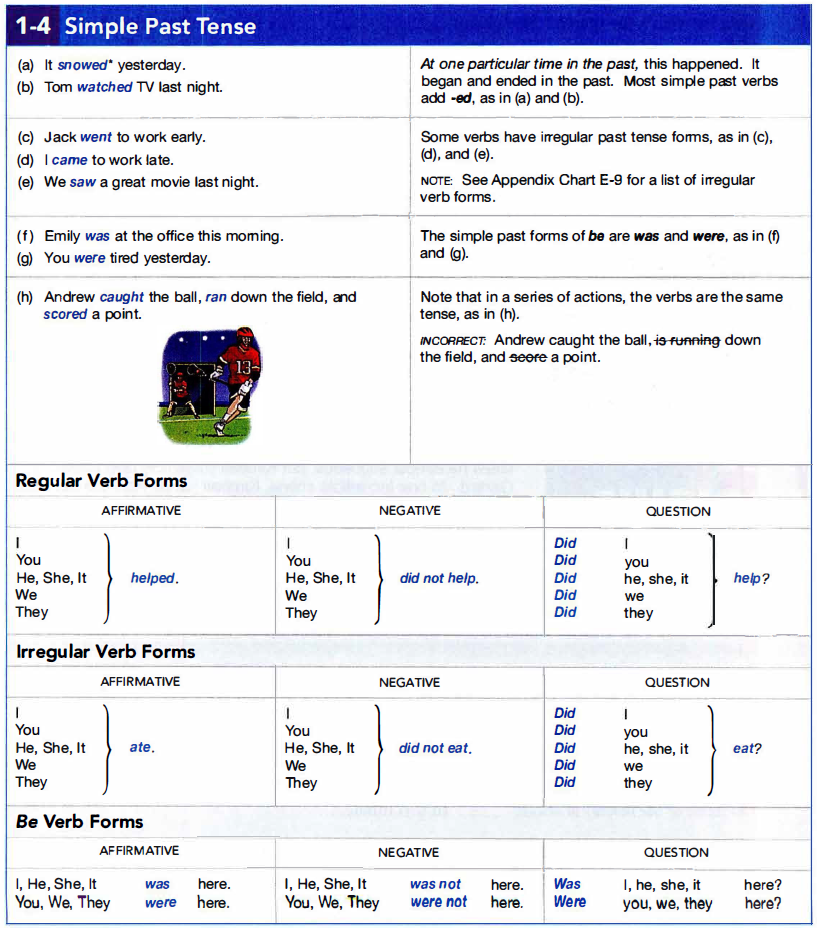
1d. Simple Past Tense
1e. Simple Past vs Past Progressive


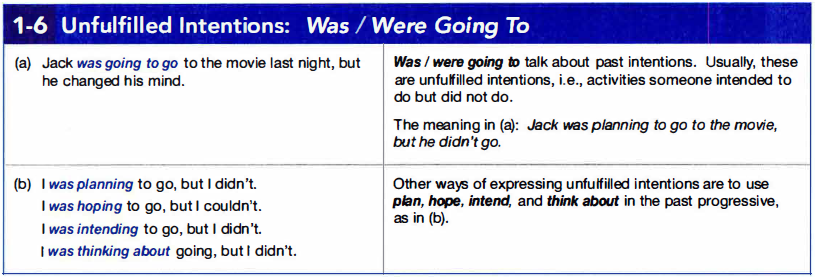
1f. Unfulfilled Intentions: Was/Were Going to
2. PERFECT AND PERFECT PROGRESSIVE TENSES

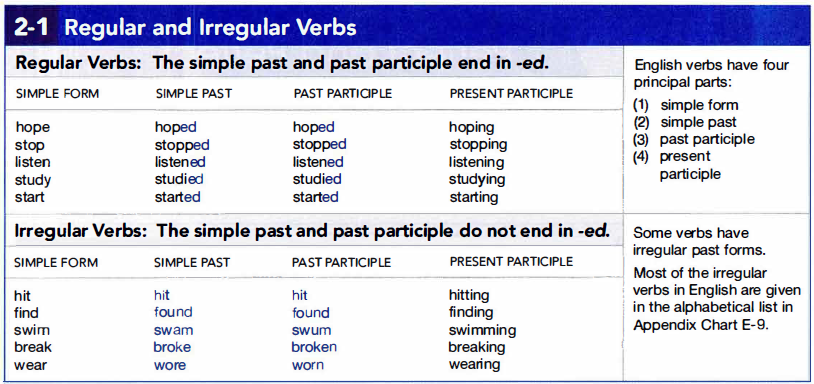
2a. Regular and Irregular Verbs
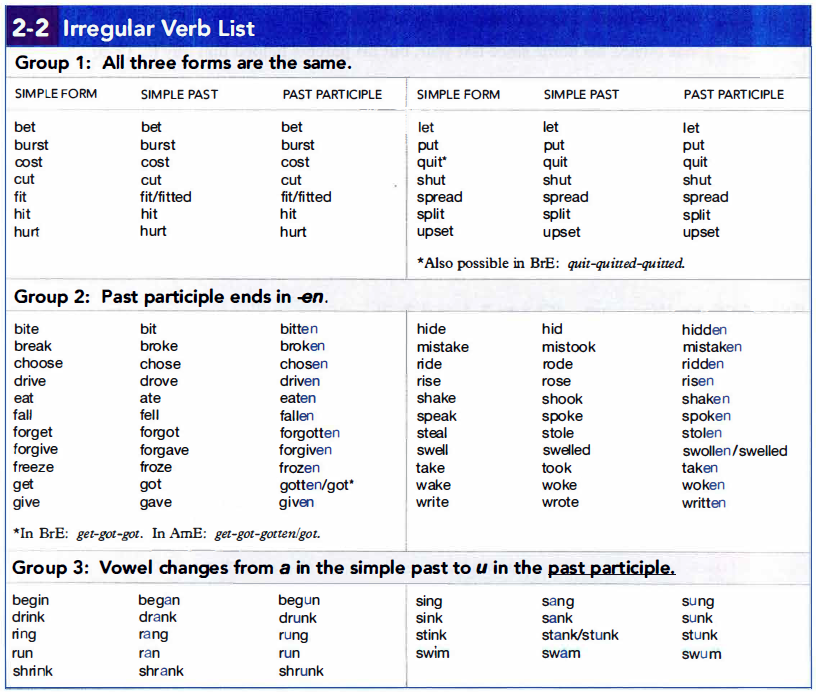
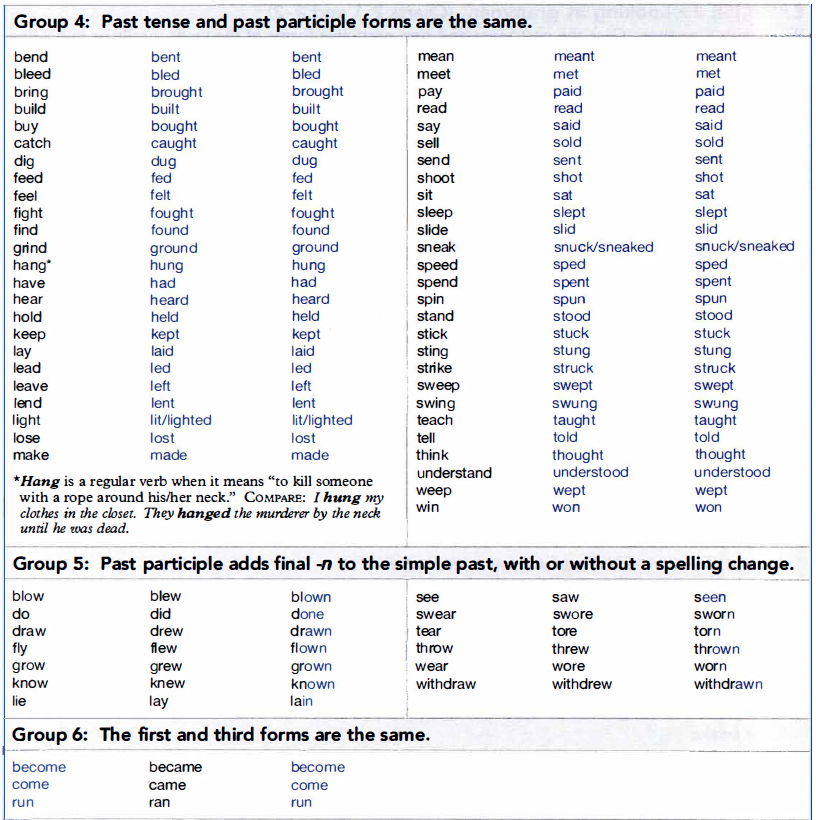
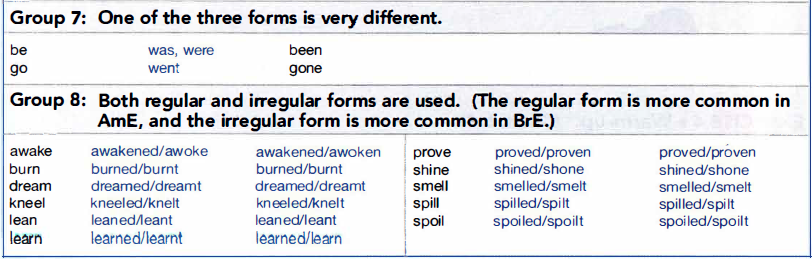
2b. Irregular Verb List
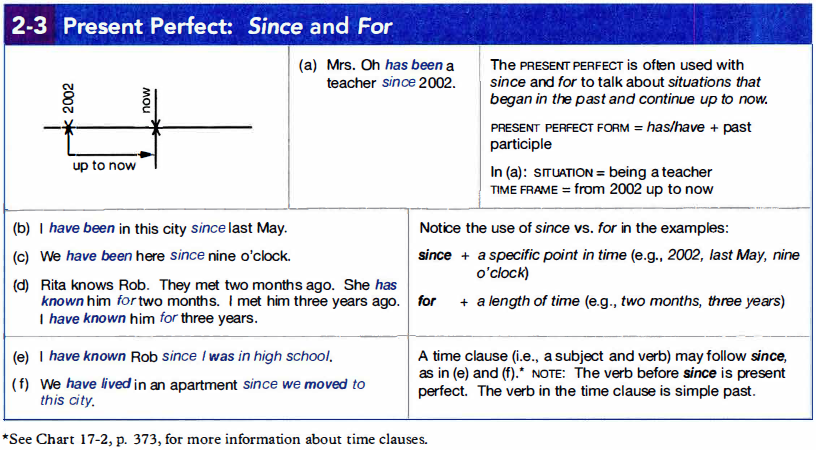
2c. Present Perfect: Since and For

2d. Present Perfect: Unspecified Time and Repeated Events
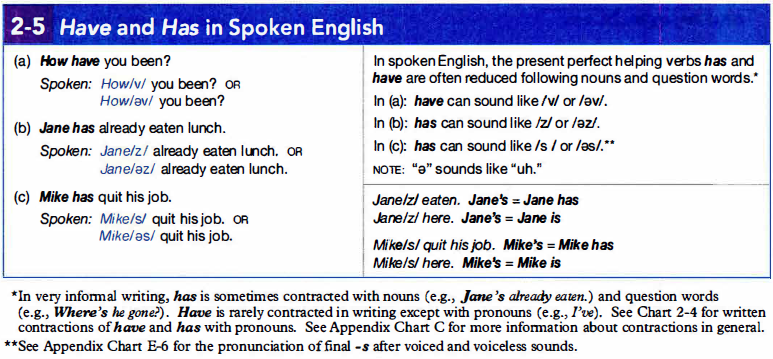
2e. Have and Has in Spoken English
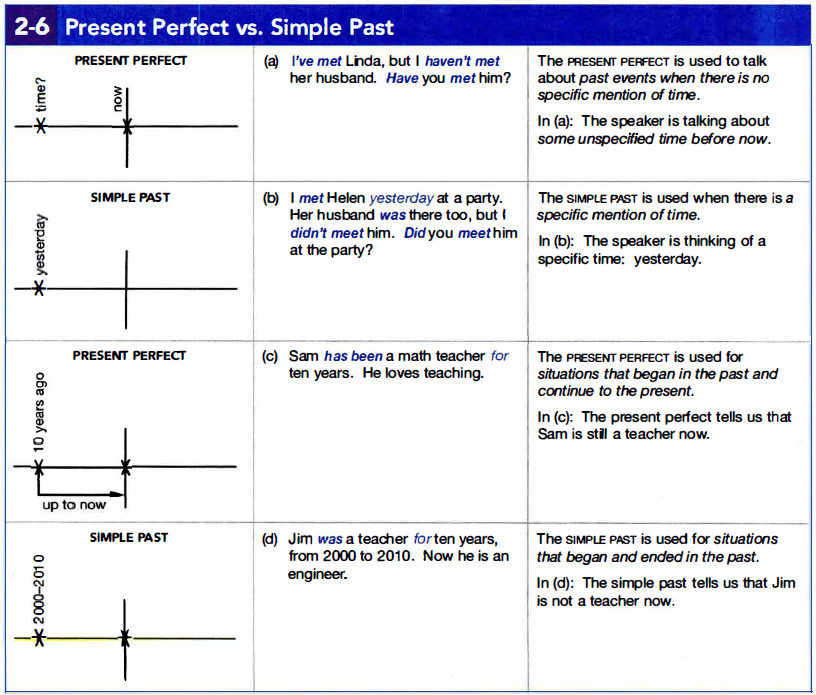
2f. Present Perfect vs Simple Past
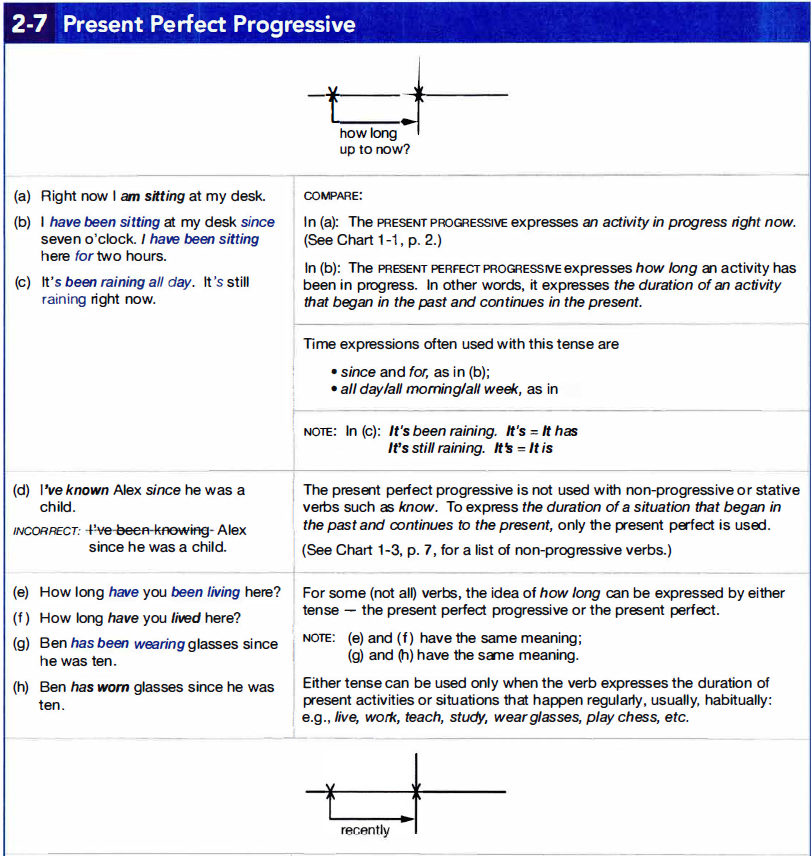
2g. Present Perfect Progressive


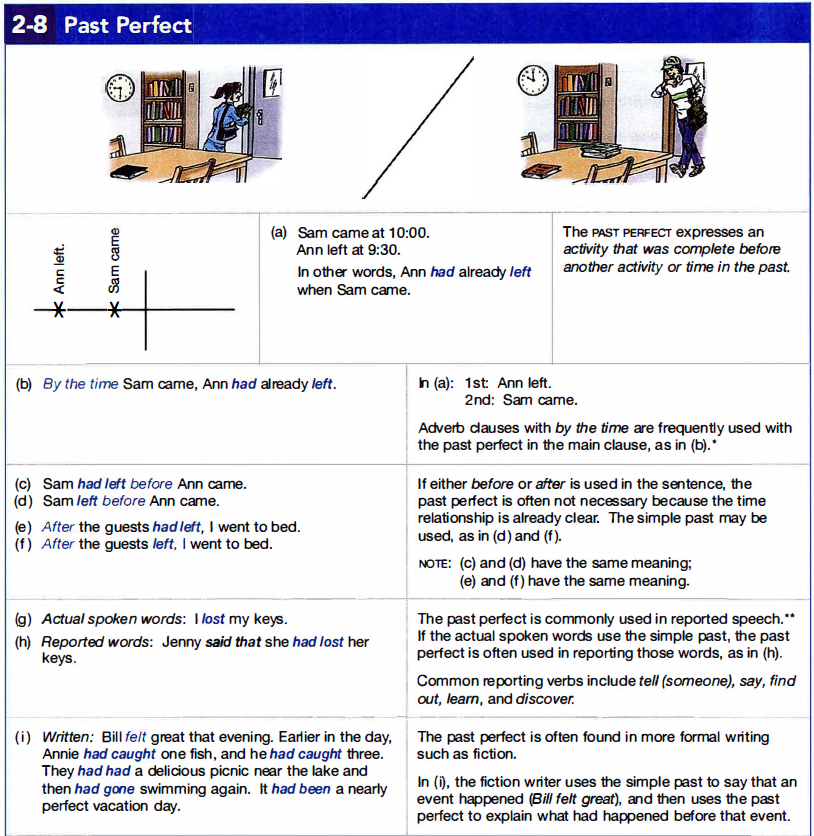
2h. Past Perfect

2i. Had in Spoken English

2j. Past Perfect Progressive

3. FUTURE TIME
3b. Will vs. Be Going To
3c. Expressing the Future in Time Clauses
3d. Using the Present Progressive and the Simple Present to Express Future Time
3e. Future Progressive
3f. Future Perfect and Future Perfect Progressive
4. REVIEW OF VERB TENSES
5. SUBJECT-VERB AGREEMENT
5a. Final -s/-es: Use and Spelling
5b. Basic Subject-Verb Agreement
5c. Collective Nouns
5d. Subject-Verb Agreement: Using Expressions of Quantity
5e. Subject-Verb Agreement: Using There+Be
5f. Subject-Verb Agreement: Some Irregularities
6. NOUNS
6a. Regular and Irregular Plural Nouns
6b. Nouns as Adjectives
6c. Possessive Nouns
6d. More About Expressing Possession
6e. Count and Noncount Nouns
6f. Noncount Nouns
6g. Some Common Noncount Nouns
6h. Expressions of Quantity used with Count and Noncount Nouns
6i. Using A Few and Few; A Little and Little
6j. Singular Expressions of Quantity: One, Each, Every
6k. Using Of in Expressions of Quantity
7. ARTICLES
7a. Articles (A,An,The) with Indifinite and Definite Nouns
7b. Articles: Generic Nouns
7d. General Guidelines for Article Usage
7e. Using The or O with Titles and Geographic Names
8. PRONOUNS
8a. Pronouns and Possessive Adjectives
8b. Agreement with Generic Nouns and Indefinite Pronouns
8c. Personal Pronouns: Agreement with Collective Nouns
8d. Reflexive Pronouns
8e. Using You, One, and They as Impersonal Pronouns
8g. Common Expressions with Other
9. MODALS, PART1
9a. Basic Modal Introduction
9b. Expressing Necessity: Must, Have To, Have Got To
9c. Lack of Necessity (Not Have To) and Prohibition (Must Not)
9d. Advisability/Suggestions: Should, Ought To, Had Better, Could
9e. Expectation: Be Supposed To / Should
9f. Ability: Can, Know How To, and Be Able To
9g. Possibility: Can, May, Might
9h. Requests and Responses with Modals
9i. Polite Requests with Would You Mind
9j. Making Suggestions: Let's, Why Don't, Shall I / We
10. MODALS, PART2
10a. Using Would to Express a Repeated Action in the Past
10b. Expressing the Past: Necessity, Advisability, Expectation
10c. Expressing Past Ability
10d. Degress of Certainty: Present Time
10e. Degress of Certainty: Present Time Negative
10f. Degress of Certainty: Past Time
10g. Degrees of Certainty: Future Time
10i. Combining Modals with Phrasal Modals
10j. Expressing Preference: Would Rather
10k. Summary Chart of Modals and Similar Expressions
11. THE PASSIVE
11a. Active vs Pasive
11c. Using the Passive
11e. Stative (Non-Progressive) Passive
11f. Common Stative (Non-Progressive) Passive Verbs + Prepositions
11g. The Passive with Get
11h. -ed/-ing Adjectives
12. NOUN CLAUSES
12a. Introduction
12b. Noun Clauses with Question Words
12c. Noun Clauses with Whether or If
12d. Question Words Followed by Infinitives
12e. Noun Clauses with That
12f. Quoted Speech
12g. Reported Speech
12h. Reported Speech: Modal Verbs in Noun Clauses
12i. The Subjunctive in Noun Clauses
13. ADJECTIVE CLAUSES
13a. Adjective Clause Pronouns Used as the Subject
13b. Adjective Clause Pronouns Used as the Object of a Verb
13c. Adjective Clause Pronouns Used as the Object of a Preposition
13d. Using Whose
13e. Using Where in Adjective Clauses
13f. Using When in Adjective Clauses
13g. Using Adjective Clauses to Modify Pronouns
13h. Punctuating Adjective Clauses
13i. Using Expressions of Quantity in Adjective Clauses
13j. Using Which to Modify a Whole Sentence
13k. Reducing Adjective Clauses to Adjective Phrases
14. GERUNDS AND INFINITIVES PART1
14a. Gerunds and Infinitives: Introduction
14b. Common Verbs Followed by Gerunds
14c. Common Verbs Followed by Infinitives
14d. Infinitives with Objects
14e. Common Verbs Followed by Either Infinitives or Gerunds
14f. Using Gerunds as the Objects of Prepositions
14g. Go + Gerund
14h. Special Expressions Followed by -ing
14i. It + Infinitive; Gerunds and Infinitives as Subjects
14j. Reference List of Verbs Followed by Infinitives
14k. Reference List of Verbs Followed by Gerunds
14l. Reference List of Preposition Combinations Followed by Gerunds
15. GERUNDS AND INFINITIVES PART2
15a. Infinitive of Purpose: In Order To
15b. Adjectives Followed by Infinitives
15c. Using Infinitives with Too and Enough
15d. Passive Infinitives and Gerundss: Present
15f. Using Gerunds or Passive Infinitives Following Need
15g. Using Verbs of Perception
15i. Using Causative Verbs: Make, Have, Get
15j. Using a Possessive to Modify a Gerund
16. COORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS
16a. Parallel Structure
16b. Parallel Structure: Using Commas
16c. Punctuation for Independent Clauses; Connecting Them with And and But
16d. Paired Conjunctions: Both ... And; Not Only ... But Also; Either .... Or; Neither ... Nor
17. ADVERB CLAUSES
17a. Introduction
17b. Using Adverb Clauses to Show Time Relationships
17c. Using Adverb Clauses to Show Causes and Effect
17d. Expressing Contrast (Unexpected Result): Using Even Though
17e. Showing Direct Contrast: While
17f. Expressing Conditions in Adverb Clauses: If-Clauses
17g. Shortened If-Clauses
17h. Adverb Clauses of Condition: Using Whether Or Not and Even If
17i. Adverb Clauses of Condition: Using In Case
17j. Adverb Clauses of Condition: Using Unless
17k. Adverb Clauses of Condition: Using Only If
18. REDUCTION OF ADVERB CLAUSES TO MODIFYING ADVERBIAL PHRASES
18a. Introduction
18b. Changing Time Cluases to Modifying Adverbial Phrases
18c. Expressing the Idea of “During the Same Time” in Modifying Adverbial Phrases
18d. Expressing Cause and Effect in Modifying Adverbial Phrases
18e. Using Upon + -ing in MOdifying Adverbial Phrases
19. CONNECTIVES THAT EXPRESS CAUSE AND EFFECT, CONTRAST, AND CONDITION
19a. Introduction
19b. Using Because Of and Due To
19c.Cause and Effect: Using Therefore, Consequently, and So
19d. Summary of Patterns and Punctuation
19e. Other Ways of Expressing Cause and Effect: Such ... That and So ... That
19f. Expressing Purpose: Using So That
19g. Showing Contrast (Unexpected Result)
19h. Showing Direct Contrast
19i. Expressing Conditions: Using Otherwise and Or (Else)
20. CONDITIONAL SENTENCES AND WISHES
20b. Expressing Real Conditions in the Present or Future
20c. Unreal (Contrary to Fact) in the Present or Future
20d. Unreal (Contrary to Fact) in the Past
20f. Using “Mixed Time” in Conditional Sentences
20g. Omitting If
20h. Implied Conditions
20i. Wishes About the Present and Past
20j. Wishes About the Futures; Use of Wish + Would
























